So you've got a brand new SSD. You installed a system on it, armed yourself with an optimization guide found on the net, and after a couple of hours you did everything possible to ... slow down your work in the system!
Don't believe? Think about what constitutes high performance. Advantages SSD speeds you can experience in three categories:
- system, for example, the speed of its loading and operation
- programs, including web surfing and working with documents, images and media files
- your actions, including disk navigation and copy/move files
How myths are born
I'm pretty sure that your SSD tuning measures have negatively affected at least one of these components. You will learn why this happened next, but first about the reasons for this optimization.
If you read the inscription "buffalo" on the cage of an elephant ...
 There are tons of guides and even tweaks on the web to optimize your SSD. In fact, the same information is used everywhere, and:
There are tons of guides and even tweaks on the web to optimize your SSD. In fact, the same information is used everywhere, and:
- obsolete, since it is aimed at saving disk space and reducing the number of rewrite cycles, which is irrelevant for modern SSDs in home PCs
- useless, because Windows itself takes care of what they offer to configure
- harmful, because it leads to a decrease in the speed of work - yours, programs and system
look critical to your guide or tweaker and think about which items fit into one of those categories!
There is another problem - bad presentation of information including misplaced accents.
If you have an HDD alongside an SSD, measure the speeds of both drives and keep the picture in mind. I will return to her, and more than once!
Special Notes for Dissenters
After the publication of the material, I decided to specifically clarify a few points so as not to repeat them regularly in the comments when answering opponents.
In this article:
- All myths are considered solely from the point of view of speeding up the system, programs and user. If a measure is declared useless or harmful, it means that it does nothing to speed up the work.
- Reducing the amount of writes to disk is not considered as an optimization measure due to the irrelevance of this approach. If this is your goal, myths 3 - 11 are for you, as well as storing an SSD in a sideboard.
- RAM disk usage is not considered as it is not directly related to SSD optimization. If you have an excess of RAM, you can use the RAM disk regardless of the type of drives installed in your PC.
- All recommendations are given taking into account a wide audience, i.e. most users. When analyzing tips, keep in mind that they may not match your tasks, work skills, and ideas about the optimal and competent use of the operating system.
Now - let's go! :)
myths
1. Disable SuperFetch, ReadyBoot and Prefetch
This advice: debatable, can slow down the launching of programs, and in Windows 10 - increase the amount of disk writing and reduce the overall performance of the OS when there is not enough RAM
The speed of launching programs from the hard drive
When each program is launched, the prefetcher checks for the presence of a trace (.pf file). If one is found, the prefetcher uses links to the file system's MFT metadata to open all necessary files. It then calls a special memory manager function to asynchronously read data and code from the trace that is not currently in memory. When the program is started for the first time or the startup script has changed, the prefetcher writes a new trace file (highlighted in the figure).
It is unlikely that SuperFetch is capable of speeding up the launch of programs from an SSD, but Microsoft does not disable the feature, given the presence of hard drives in the system. If a proprietary SSD manufacturer's utility (such as the Intel SSD Toolbox) recommends disabling SuperFetch, follow its advice. However, in this case it is more than logical to keep all programs on the SSD, which will be discussed below.
Compress memory in Windows 10
This aspect is covered in a separate article Nuances of disabling the SysMain service in Windows 10. Earlier on this page there was an excerpt from it, published impromptu.
2. Disable the Windows Defragmenter
This tip: useless or harmful, may degrade disk performance
One of the functions of the CheckBootSpeed utility is to check the status of a scheduled defragmentation job and the Task Scheduler service. Let's see how these parameters are relevant for the latest Microsoft OS installed on the SSD.
Windows 7
Windows 7 does not defragment the SSD, which is confirmed by the words of the developers in the blog.
Windows 7 will disable defragmentation for SSD drives. Because SSDs excel at random reads, defragmenting won't provide the same benefits that it does on a regular drive.
If you don't believe the developers, take a look at the event log. You won't find any entries there about defragmenting an SSD volume.
So when the SSD is the only drive, the scheduled task simply doesn't run. And when the PC also has a HDD, disabling a task or scheduler deprives the hard drive of decent optimization with a standard defragmenter.
Windows 8 and newer
In Windows 8, the place of the defragmenter was taken by the disk optimizer!
Optimizing hard drives, as before, comes down to defragmentation. Windows no longer ignores solid state drives, but helps them by sending the controller additional a set of TRIM commands for the entire volume at once. This happens according to the schedule as part of automatic maintenance, i.e. when you're not working on a PC.
Depending on the SSD controller, garbage collection can be performed immediately upon receipt of the TRIM command, or delayed until a period of inactivity. By disabling the disk optimizer or task scheduler, you reduce the performance of the drive.
3. Disable or move the paging file
This tip: useless or harmful, reduces the speed of the system when there is not enough memory
The hardware configuration must be balanced. If you don't have enough RAM installed, you should add more, as an SSD only makes up for some of the lack of RAM by speeding up swapping compared to a hard drive.

When you have enough memory, the swap file is practically not used, i.e. This will not affect the life of the disk in any way. But many people still turn off paging - they say, let the system keep everything in memory, I said! As a result, the Windows memory manager does not work in the most optimal mode (see #4).
In extreme cases, the paging file is transferred to the hard drive. But if suddenly the memory is not enough, you will only benefit in performance by having pagefile.sys on the SSD!
IN Q: Do I need to put the swap file on the SSD?
ABOUT: Yes. The main operations with the swap file are random writes of small volumes or sequential writes of large data arrays. Both types of operations work great on an SSD.
Analyzing telemetry focused on evaluating writes and reads for the swap file, we found that:
- reading from Pagefile.sys prevails over writing to pagefile.sys in a ratio of 40:1,
- read blocks for Pagefile.sys are usually quite small, 67% of them are less than or equal to 4 KB, and 88% are less than 16 KB,
- write blocks in Pagefile.sys are quite large, 62% of them are greater than or equal to 128 KB and 45% are almost exactly 1 MB
Generally speaking, the typical swap file usage patterns and SSD performance characteristics are a great fit, and it is this file that is highly recommended to be placed on an SSD.
But in practice, the desire to extend the life of an SSD at any cost is indestructible. Here is a blog reader shaking his SSD, transferring pagefile.sys to the hard drive, although he himself even sees with the naked eye that this reduces performance. By the way, my netbook cannot install more than 2 GB of memory, and with a solid state drive it became much more comfortable than with a standard 5400 rpm HDD.
Finally, don't forget that completely disabling the swap file will prevent you from performing critical error diagnostics. The paging file size can be flexibly adjusted, so you always have a choice between disk space and performance.
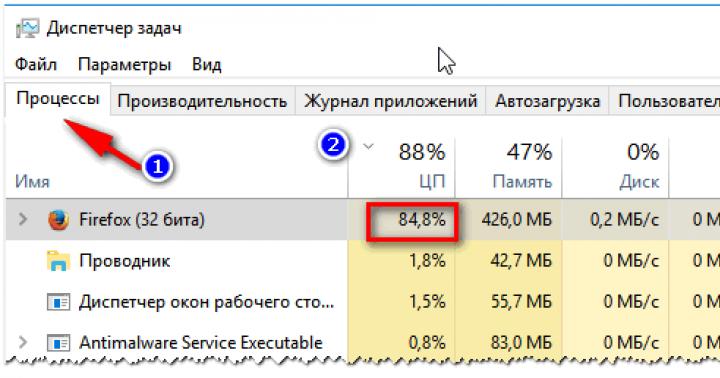
Tricky question: what was my swap file size when i took the task manager screenshot?
Special note
On the Internet (including in the comments to this entry) you can often find the statement: “The paging file is not needed if you have installed N GB RAM. Depending on fantasy N takes the value 8, 16, or 32. This statement does not make sense, because it does not take into account the tasks that are performed on a PC with a given amount of memory.
If you set yourself 32GB, and 4-8GB is used, then yes, you don’t need FP (but then it’s not clear why you bought 32GB RAM :). If you have purchased such an amount of memory in order to use it as much as possible in your tasks, then the FP will come in handy for you.
4. Disable hibernation
This advice: vague and harmful to mobile PCs, can reduce battery life and speed of your work
I would put my advice like this:
- stationary PCs - shutdown is normal, because you might as well use sleep
- mobile PCs - turning off is not always advisable, especially when the battery consumption is high during sleep
However, people have disabled, are disabling and will disable system protection regardless of the type of disk, this is already in the blood! And no, I don't want to discuss this topic in the comments for the hundredth time :)
6. Disabling Windows search and/or disk indexing
This tip: useless, slows down your work
This is sometimes argued by the fact that SSDs are so fast that the index will not significantly speed up the search. These people just never really used real Windows search!
I believe that it is pointless to deprive yourself of a useful tool that speeds up the performance of everyday tasks.
If you have fallen victim to any of these myths, tell me in the comments if I managed to convince you of their futility or harm and in what cases. If you don't agree with my assessment of "optimization", explain what is the benefit of these actions.
You can mark fragments of text that are interesting to you, which will be available via a unique link in the browser's address bar.
about the author
Vadim, in recent days I have bought 4 SSDs for installation in all my computers. Let's just say... life has changed :-)
I also thought for a long time whether to buy a laptop with an SSD or a hybrid drive, the second one won, I chose 340GB + 24 SSD. I was surprised that the standard installation of Windows 8 was on a 5400 drive, but not an SSD. After suffering for a long time, I moved Windows 8 to an SSD and went a little crazy, because. about 3 GB left on the SSD. Knowing that W8 will swell over time and will have to fight for space, I returned everything back, transferred TEMP and Page file to SSD, plus I put frequently run programs.
Still, you just had to buy a laptop with an SSD and not soar your brain. They gave me an SSD for NG and now I'll stuff it into an old netbook, install W8 and be happy.
Thanks for the articles about SSD, we have the whole department reading.
Alexei
You, Vadim, have gone through SSD myths very well, we can hope that now there will be fewer fans of SSD perversions. I have Win8 on an SSD, as I installed it and it plows, I’m satisfied and don’t bother my head with all sorts of optimizations, the exhaust from which is doubtful.
PS: Answer to the question: 1Gb.
-
Alexey, thanks for the response. You can’t put your head on everyone, but I don’t try :)
The answer to the question is incorrect. How did you come to him?
madgrok
Before buying an SSD, I read a mountain of forums, benchmarks, etc. And I came to the conclusion that all the tweaks are in the furnace.
Why do people buy their own SSD? Of course, what would be faster! :) And most of the optimization tweaks basically negate the entire performance gain, which Vadim wrote about.
I use my Vertex 4 256 GB as a regular disk for the system. Bought somewhere in the fall. The flight is excellent, health is 100%
An excellent article, I will recommend it to all my friends, friends for reading so as not to suffer. :)
And in general, thanks to the author for a great blog. I really like the fact that the topic is trying to "disassemble the bones."
Andrey
Vadim, at the end of the article there is a survey about the presence of SSD on our computers, I think that this topic is still relevant - there are those who are not going to, at least in the near future, acquire a solid state drive for a number of reasons - someone does not see the point of installing it on an old one they save up a computer for a new one, or, as in the polling point, arranges an HDD, or this is how Pavel Nagaev thinks for a long time which one to prefer ....
What would you advise? Is it worth moving the OS to an SSD for "increasing system performance", so to speak?
Andre
Hello Vadim, I think a lot of people are now looking at buying an SSD, and it would be very cool if you wrote an article on choosing an SSD!
Alexey Matashkin
Vadim, thanks for the article.
In my practice, I did not have to deal with these myths, I only heard some advice separately, so I read it with pleasure.
I don’t quite get into the survey :) The main PC is not home, and it has an SSD. And at home, there is still enough of the usual.
There is nothing to add on questions, because I don’t use tweaks, all installed SSDs work normally with the system.
Although, an important detail is updating the firmware on the disk. In my practice, there are 3 cases of serious failures that were eliminated with firmware version updates.
Valentine
Pavel Nagaev,
Your 24 SSD was most likely designed for caching, which is why it is so small, maybe you needed to use it as a cache, in which case you get the benefits of both media - volume and speed. Vadim, do you have an article regarding hybrid hard drives or combining HDD with SSD? I think many readers might be interested in such an article. I think the topic of 12 myths is very useful, because I have many friends who consider themselves experts, but make such mistakes and impose these mistakes on ordinary users, thanks to the link to this article, it will be possible to convince them to make such mistakes
Vadims Podans
Nice and good article.
Sergey
Yes, indeed, people are surprised who buy an SSD to speed up work, but then they themselves transfer everything and turn it off and lose performance again ..
MythBusters in action! We went through all these myths with a skating rink.
Alexey G
At first I fell for disabling hibernation, but then I realized that it was inconvenient.
I remove labels 8.3. Because I use new versions of the program, and I don't need it)
From life: when I build a PC with an SSD, I transfer user files to the HDD. If the PC for unknown reasons (playful hands, viruses) starts not to boot, then if I am nearby, then I will restore the customized image of the installed system (thanks to the blog), but if the person called another “master”, then the first thing he will do is format the disk: (More Unfortunately, I have not seen a smart way in my city, so this is a forced need to save the user's files.
Answer to the question: 2834mb?
Dima
Thanks Vadim.
As always intelligible and with a light sense of humor.
As promised, I part with the myths easily and see you off on your last journey. I'll turn everything back on.
Sincerely, Dima.
PGKrok
I agree on all points, but I myself had to transfer the index files, some programs and personal photo-videos to the HDD, because. SSD - only 60 GB (which one I mastered :))
For comparison (to the question of "keeping the picture in mind")
Result CrystalDiskMarc (HDD)
http://pixs.ru/showimage/HDD1301020_6347406_6812031.png
Result CrystalDiskMarc (SSD)
http://pixs.ru/showimage/OSZ3010201_4238885_6812055.png
controller SATA-3 SSD - SATA-6
Dawn
I bought a 60gb ssd, left only Windows 8, program files, appdata, program data on it. The rest is on hdd.
Reason: the system partition is growing too fast, just look, the place will go to zero.
When buying, there was one task: to speed up the cold boot of the system. What he achieved - 8 seconds.
Vadim, the article is a test, thanks!
Ruby
About transferring TEMP and cache - I stupidly put them on a gigabyte ramdisk - this is a real speed increase, incomparable with SSD.
Denis Borisych
I have been working in IT for a long time and still do not cease to be surprised at the grief of optimizers.
I have had an ssd in my home computer for a year now and everything is in a bunch. 7 starts in 10 seconds, programs load quickly and easily without any optimizations. Well, except that the folder of necessary and important documents is not on ssd (its size is over 500 GB). And in the folder "My Documents" there is usually a routine.
As a person, well, I am very close to IT, sometimes I am not enthusiastic about the innovations of MS (only the inability to use Explorer without a mouse is worth something). But I must objectively admit that in terms of optimizing the operation of the OS on ssd and stability of work, they are undoubtedly great.
Ruby
I would also transfer the search index, but on the Windows blog they write that it is still kept in memory, so it makes no sense.
SuperFetch is needed in any case, it preloads files into RAM in advance, increasing speed and reducing the number of accesses to the drive.
Valery
Vadim, I read your articles quite regularly and often put the advice from them into practice.
Having bought an SSD (Intel 520 120GB), I also first read about all sorts of optimizations and even applied some, but now I left only the indexing transferred to the HDD and Intel's recommendations for their disks, and here some of your advice and recommendations from Intel diverge:
http://123foto.ru/pics/01-2013/42746566_1358157387.jpg
Whom to listen to?))
Alexei
Vadim Sterkin,
Came by typing :-)
My swap file takes up 1 Gb per 16Gb of RAM (the size of the system's choice). Moreover, the system monitor shows almost zero% load. I decided that 8Gb should have at least 1Gb.
Oleg
Hello Vadim. I always look forward to new articles from you, this article was VERY useful for me and for my friends. To my regret, my arguments and advice do not reach some friends, for some reason they trust more forums where they do not always write useful information.
I hope this article will convince you.
I will wait for articles about choosing an SSD.
Thank you.
George
Thank you for the article.
To be honest, I didn’t quite understand about Superfetch - what is the increase in performance on an SSD?
And about the size of the swap file, the answer seems to be this: 10.7 GB is written in the allocated line. From this figure, you must subtract the amount of RAM.
Alexander
I recently bought a Kingston Hiper X 3K 120GB SSD. I installed Seven sp1. I did not see any increase in download speed and program operation.
Previous configuration: Asus P5Q, 2 WD 500Gb Raid 0, DDR2 2 1GB each.
My conclusion: when connecting an SSD to a "slow" Sata 3Gb / s port, the performance gain of the system, compared to that set to stripping, is negligible. You will have to upgrade to a motherboard with Sata 6Gb / s and at least 8GB DDR3 memory.
GlooBus
Pavel Nagaev,
From 16-32 GB SSD disks soldered on laptop motherboards, there is no sense. The best thing in this case would be to take a laptop in a simple configuration with an HDD and upgrade it yourself. I did just that, took the ASUS X301A with 2 GB of memory, 320 GB of HDD and upgraded to 8 GB of memory and 128 GB of SSD. The laptop worked in a completely different way! Loading the computer from pressing the button until the password entry window appears is 6-7 seconds. I didn’t do any tweaks, except that I turned off indexing, tk. I don't use search.
Alick
The other day I installed VERTEX 4 128Gb Win 8 on it, applied optimizers, and after a week I realized that it was in vain, incl. will have to be reinstalled. And here's another great article.
Michal
Vadim Sterkin,
I think this is due to the fact that most people simply have not yet had a specific practice in using an SSD, like you have.
and there are many myths.
for example, I'm from Uzbekistan, we have SSDs here that have just appeared.
no experience with them yet. yes, and very expensive.
I read your article, I realized that in vain I transferred the swap file.
thanks for the article, I hope not the last :)
Frequently Asked Questions about Solid State Drives
Before answering questions, we would like to remind you that we believe that SSDs for laptops and desktops (as well as for enterprise servers) have a great future ahead of them. SSD is really able to provide high performance, improved system response, longer battery life, high reliability, faster boot, less vibration and noise. As prices drop and drive quality rises, we believe more computers will be sold with SSDs instead of traditional hard drives. With this in mind, we have concentrated the necessary engineering efforts to ensure that users can fully experience the benefits of working with a new type of storage device.
Q: Will Windows 7 support tweaking?
Oh yeah. This has already been discussed above.
Q: Will defragmentation be disabled by default for SSDs?
Oh yeah. The automatic start of the defrag task will not include partitions created on the SSD or identifying themselves as such. In addition, if the system partition shows a random read performance higher than 8 MB / s, it will also be excluded from the list for defragmentation. The performance level was determined as a result of internal testing.
The threshold performance test was added to the final version due to the fact that only a few of the SSDs on the market identify themselves as SSDs in the system. 8 Mb / s is quite modest. SSD performance ranges from 11 to 130 MB/s. We tested 182 hard drives, and only 6 of them exceeded the 2 MB/s bar in the random read test. The results of the remaining 176 lie between 0.8 and 1.6 Mbps.
Q: Will Superfetch be disabled for SSDs?
A: Yes, for most computers with SSD. If the drive is an SSD, and if it performs adequately with random write/rewrite, then Superfetch, Prefetch for loading and running applications, ReadyBoost and ReadyDrive will be disabled.
Initially, these features were supposed to be disabled for all SSDs, but we have found that this results in performance degradation on some systems. While investigating the possible reasons for this situation, we found that some early SSD models had serious random write problems, eventually leading to the fact that reading from the disk stopped altogether and for a long time. With Superfetch and Prerefetch turned on, day-to-day performance is again noticeably improved.
A: Compressing files helps save disk space, but it requires additional CPU power to compress and decompress, which leads to increased power consumption on portable PCs. Strictly speaking, for folders and files that are used very rarely, compression can be a good tool to save expensive space on an SSD - in case the free space is really so necessary.
However, we do not recommend using compression in cases where folders and files are in constant use. Your Documents folders and the files in them are not a problem, but temporary Internet folders and mail directories should not be compressed, because they are constantly writing and overwriting a large number of files in batch mode.
Q: Does the Windows Search Indexer work differently on an SSD?
Q: Has the Bitlocker encryption procedure been optimized to work with SSDs?
A: Yes, on NTFS. When Bitlocker is first configured for a particular partition, it is read in its entirety, encrypted, and written back. As soon as this happens, the file system will issue a command to perform an adjustment that optimizes the performance of the drive.
We encourage all users who are concerned about the safety and security of their data to enable Bitlocker on their drives, including SSDs.
Q: Does Media Center take any special action when configured on an SSD?
Oh no. Although SSDs have advantages over traditional HDDs, the price per GB for SSDs is still significantly higher than for regular drives. For most users, a multimedia-optimized HDD remains the best option for now, as such content involves significant write and playback workloads that have sequential read/write characteristics.
Q: Does SSD write caching make sense, and how does Windows 7 help support write caching if the SSD supports it?
A: Some manufacturers install RAM chips on their devices for more than just controllers; they should, as with traditional disks, cache reads and, if possible, writes. For drives that cache writes in fast, non-volatile memory, Windows 7 assumes that having overwrite commands and write sequencing will be no less efficient than for HDDs. In addition, Windows 7 assumes that user settings that disable caching will be treated by the SSD in the same way as if it were a regular drive.
Q: Does it make sense to set up RAID for SSDs?
Oh yeah. The reliability and performance gained by configuring RAID on traditional drives is maintained when using an SSD.
Q: Do I need to put the swap file on the SSD?
Oh yeah. The main operations with the swap file are random writes of small volumes or sequential writes of large data arrays. Both types of operations work great on an SSD.
Analyzing telemetry focused on evaluating writes and reads for the swap file, we found that:
reading from Pagefile.sys prevails over writing to pagefile.sys in a ratio of 40:1,
read blocks for Pagefile.sys are usually quite small, with 67% of them less than or equal to 4 KB, and 88% less than 16 KB.
The write blocks in Pagefile.sys are quite large, with 62% of them being greater than or equal to 128 KB and 45% being almost exactly 1 MB.
Generally speaking, the typical swap file usage patterns and SSD performance characteristics are a great fit, and it is this file that is highly recommended to be placed on an SSD.
Q: Are there any restrictions for using hibernation with an SSD?
A: No, hiberfile.sys is written and read sequentially in large blocks, and can be located on both SSD and HDD.
Q: What changes have been made to the Windows Experience Index to properly reflect SSD performance metrics?
A: In Windows 7, these are new random write, overwrite, and read evaluation criteria. The best samples can get an index from 6.5 to 7.9. To fall into this range, drives must have outstanding performance in these types of operations and be resistant to heavy loads of this type.
During beta testing of Windows 7, there were cases where the index varied from 1.9 to 2.9, or as if the disk (SSD or HDD) did not work at all, as expected, when performing a performance assessment. We received a lot of feedback on this issue, most objected to such low ratings. As a result, we simply banned SSDs with potential performance issues from competing for the 6.0+ and 7.0+ grades that were recently added. SSDs that aren't among the favorites of this kind of race will get indexes roughly the same as they would have in Windows Vista, without taking much advantage of the random write performance boost in Windows 7.
Michael Fortin,
Fundamentals Program Manager
Hello!
After installing an SSD drive and transferring a copy of Windows to it from your old hard drive, the OS must be configured (optimized) accordingly. By the way, if you installed Windows from scratch on an SSD drive, then many services and parameters will be configured automatically during installation (for this reason, many recommend installing a “clean” Windows when installing an SSD).
Optimizing Windows for an SSD will not only increase the life of the disk itself, but also slightly increase the speed of Windows. By the way, about optimization - the tips and recommendations from this article are relevant for Windows: 7, 8 and 10. And so, perhaps, let's start ...
1) Is ACHI SATA mode enabled
how to enter bios -
You can check in which mode the controller is working quite simply - look at the BIOS settings. If the disk works in ATA, then you need to switch its operating mode to ACHI. True, there are two nuances:
First - Windows will refuse to boot, because. it does not have the necessary drivers for this. You need to either install these drivers beforehand, or simply reinstall Windows (which is preferable and easier in my opinion);
The second caveat is that you may simply not have ACHI mode in your BIOS (although, of course, these are already somewhat outdated PCs). In this case, most likely, you will have to update the BIOS (at least, study the official website of the developers - is there such an opportunity in the new BIOS).

Rice. 1. AHCI working mode (DELL laptop BIOS)
By the way, it will also not be superfluous to go to device Manager(can be found in the Windows Control Panel) and open the tab with IDE ATA/ATAPI controllers. If there is a controller in the name of which there is “SATA ACHI”, then everything is in order.
AHCI operating mode is required to support normal operation TRIM SSD drive.
REFERENCE
TRIM is an ATA interface command that is necessary for Windows to tell the drive which blocks are no longer needed and can be overwritten. The fact is that the principle of deleting files and formatting in HDD and SSD drives is different. When using TRIM, the speed of the SSD disk increases, and uniform wear of the disk memory cells is ensured. TRIM is supported by Windows 7, 8, 10 (if you use Windows XP, I recommend updating the OS, or buying a disk with hardware TRIM).
2) Is TRIM support enabled in Windows OS
To check if TRIM support is enabled in Windows, just run the command prompt as an administrator. Next, enter the command and press Enter (see Fig. 3) .
If DisableDeleteNotify = 0 (as in Fig. 3), then TRIM is enabled and nothing more needs to be entered.
If DisableDeleteNotify = 1, then TRIM is disabled and you need to enable it with the command: fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0. And then check again with the command: fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify.
Windows optimization (relevant for 7, 8, 10) for SSD drive
1) Disable file indexing
Moreover, when this function is disabled, the number of records on the disk decreases, which means that its life increases. To disable indexing, go to the properties of the SSD drive (you can open Explorer and go to the “This Computer” tab) and uncheck the box next to “Allow files on this drive to be indexed…” (see Fig. 4).
2) Disable search service
This service creates a separate file index, which makes finding certain folders and files faster. An SSD drive is fast enough, and besides, many users do not practically use this feature - which means it is better to turn it off.
First open the following address: Control Panel/System and Security/Administrative Tools/Computer Management
3) Disable hibernation
When using an SSD drive, this function loses its meaning somewhat. Firstly, the Windows system already starts quickly enough with an SSD, which means there is no point in saving its state. Secondly, extra write-rewrite cycles on an SSD drive can affect its life.
Disabling hibernation is quite simple - you need to run the command prompt as an administrator and enter the command powercfg -h off.
4) Disable auto-defragmentation of the disk
Defragmentation is a useful operation for HDD drives, which helps to slightly increase the speed of work. But this operation does not bring any benefit to the SSD drive, since they are arranged a little differently. The speed of access to all cells in which information is stored on an SSD drive is the same! And this means that no matter where the “pieces” of files are located, there will be no difference in access speed!
In addition, moving "pieces" of a file from one place to another increases the number of write / rewrite cycles, which reduces the life of the SSD drive.
If you have Windows 8, 10* You don't need to disable defragmentation. Built-in disk optimizer (Storage Optimizer) will automatically determine
If you have Windows 7 - you need to go into the disk defragmentation utility and disable autorun thereof.
5) Disable Prefetch and SuperFetch
Prefetch is a technology thanks to which the PC speeds up the launch of frequently used programs. It does this by loading them into memory in advance. By the way, a special file with the same name is created on the disk.
Since SSD drives are fast enough, it is advisable to disable this function, it will not give any increase in speed.
SuperFetch is a similar function, with the only difference that the PC predicts which programs you are likely to run by loading them into memory in advance (it is also recommended to turn it off).
When you open the registry editor - go to the following branch:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
Next, you need to find two parameters in this registry subkey: EnablePrefetcher and EnableSuperfetch (see Figure 8). The value of these parameters must be set to 0(as in Fig. 8). The default values for these parameters are 3.
Rice. 8. Registry Editor
By the way, if you install a Windows drive from scratch on an SSD, then these parameters will be configured automatically. True, this does not always happen: for example, failures may occur if you have 2 types of disks in your system: SSD and HDD.
Utility for automatically optimizing Windows for an SSD drive
You can, of course, manually configure all of the above in the article, or you can use special utilities for fine-tuning Windows (such utilities are called tweakers, or Tweakers). One of these utilities, in my opinion, will be very useful for owners of an SSD drive - SSD Mini Tweaker.
SSD Mini Tweaker
An excellent utility for automatically configuring Windows to work on an SSD drive. The settings that this program changes allow you to increase the operating time of the SSD by an order of magnitude! In addition, some parameters will allow you to slightly increase the speed of Windows.
Benefits of SSD Mini Tweaker:
- completely in Russian (including hints for each item);
- works in all popular OS Windows 7, 8, 10 (32, 64 bits);
- installation is not required;
- completely free.
PS
Many also recommend transferring the browser cache, swap files, Windows temporary folders, system backup (and so on) from an SSD drive to an HDD (or disable these features altogether). One small question: "why then do you need an SSD?". To just start the system in 10 seconds? In my understanding, an SSD drive is needed to speed up the system as a whole (the main goal), reduce noise and rattle, increase laptop battery life, etc. And by performing these settings, we can thereby nullify all the advantages of an SSD drive ...
That is why, by optimizing and disabling unnecessary functions, I understand only what really does not speed up the system in any way, but can affect the life time of an SSD drive. That's all, good luck to everyone.
More recently, all computers worked with HDD, with low speed and low efficiency. But they have been replaced by a new generation of drives, the so-called SSDs, which are much faster than their older counterparts. Like all new devices, at first they were expensive, and their volumes did not differ in large capacity.
But over time, manufacturers began to increase their volumes, and because of competition, the cost began to decline. It would seem, what else does an ordinary user need? But they have one
Warning: Excessive overwriting of data can completely disable it. But to avoid trouble, setting windows 7 to work optimally with SSD will help, and this will lead to an increase in the service life of the solid state drive.
Why do you need an OS setup?
All flash drives have their own memory, it is based on microcircuits. They don't have any moving parts like HDDs, so they don't take any kind of shock. SSD memory is made up of many cells that can wear out with a lot of overwriting.
And a very important point is setting up the OS to transfer data to a flash drive, since calling some services and operations from the drive is slow if windows is not configured.
The setting will reduce the use of space, accesses to it, which will certainly increase the life of the removable media. If the SSD is used in normal mode, it can last for a decade, and if you use it actively, then the period is reduced to 2 years.
To install windows on the drive, you need to prepare the system. We check:
- we go to the website of the manufacturer of the computer or SSD, check the relevance of the versions. If you intend to reflash it, then you can erase all the data, and you should know about this before installing the OS. Find information about the update, download it to your computer;
- we translate the system startup in the BIOS setup to AHCI, that is, we set the removable drive first. Use the latest modes, otherwise it will work with glitches;
- removable media must be formatted. You can use windows tools, it will cope with this task;
- you should check the system boot from removable media, connect it, create logical partitions on it. If it was previously split, then update them, delete the previous breakdown, and split again. Now install on it the latest version of the disk controller driver, previously downloaded from the manufacturer's website.
Video: Optimizing SSD Drives
Disable services and features
The many services and functions enabled by default in windows 7 slow down the system startup from an SSD, we will tell you how to disable them correctly, and which services it is not rational to disable. Since running services consume a lot of computer resources, disabling them will speed up the start, and the very operation of removable media.
Indexing and caching
To disable write cache, do the following:

The option to create a write cache in windows 7 constantly accesses the device's RAM, and records the most requested commands, and then they will be executed on removable media. But SSD is much faster than HDD, and this option is superfluous.
Indexing is useful only for the system with HDD, but for removable media it is not effective: it will not affect the speed, and the disk will serve much less, since the index data will be constantly updated.
Disabling this feature will not affect the database, and so the shutdown operation will be transparent to system startup:
- My computer;
- storage device;
- properties.
In the window that opens, uncheck the “allow indexing” option, and if the system gives you an error warning, you don’t need to return everything back, and uncheck it anyway.

defragmentation
We disable defragmentation in automatic mode, this function is not needed, it will only reduce its capabilities.
We do:

hibernation
Windows has useful power saving features: sleep mode and hibernation. These features are designed specifically for laptops that are in power saving mode.

Hibernation is the preservation of computer data during the transition to sleep mode, windows writes them down and saves them in the Hiberfil.sys folder on the HDD. When you exit this mode, all data is unloaded and the computer starts from where it left off.
If you disable this mode, then you can significantly increase the space, and if you start the system from it, then there is no need for them.
The system will start much faster, and you can disable it from the start menu:

You should run the service as an administrator of the computer, right-click, the command line opens: enter:

After these steps, the service will be disabled.
System Restore
With this function, you can roll back the system if some glitches have begun. windows creates restore points, writes everything to a separate file that takes up a lot of space. You can disable this feature, but it would be better if you limit the size of the file intended for system recovery.
To do this, open the "my computer" folder:

Prefetch and SuperFetch
SuperFetch is responsible for caching the most requested files, and this service is not needed to run from the drive and should be disabled.
The Prefetch service is responsible for loading programs into the computer's RAM, and in our case it is useless, and we disable it:

Video: Disk Setup
Moving the paging file
It is advisable to do this if the OS is 32-bit, the paging file needs to be moved to another location, you should run a number of commands:
- Control Panel;
- System;
- Additionally;
- performance;
- Options;
- Additionally;
- Virtual Memory

If your computer has 64-bit windows installed with more than 8GB of RAM, then you can safely disable the paging file option:

Is TRIM enabled?
With the TRIM command, the OS transmits important information to the SSD about unused data blocks, which can be cleared by it. Since the option to format and delete files can lead to poor performance of the drive, this feature allows you to reduce the number of unnecessary files and clean it up.
This is one of the most basic commands that must be enabled, otherwise the write level will be low, which will reduce the functionality of the disk space.
To make sure this feature is enabled:

Setting up windows 7 for an SSD drive, SSD Mini Tweaker
If you are not a computer genius, but you want to transfer the OS to an SSD, then use the small SSD Mini Tweaker utility. The program does not take up much space, but copes with its task quite quickly, and is relevant for those users who are going to transfer the launch of windows 7 system of 32 and 64 bits to SDD.
The window of the launched program looks like this, and you can immediately configure the necessary parameters.

Many functions for transferring windows are not needed, they can only slow down the process itself:

The program will help you configure about 13 parameters that will increase performance if it starts from an SSD. The purpose of optimization is to reduce access to removable media, which prolongs its performance.
Your operating system can be activated if you run it from an SSD drive, and windows 7 adapts perfectly to run from a solid state drive. Even if you have a lot of power-hungry programs installed, with proper optimization you can debug it to run from SDD, paying special attention to Superfetch/Prefetcher and defragmentation.
If you have a lot of RAM, then it's even better: you can successfully optimize it, which will only lead to speed and long life of removable media.
Solid state drives are becoming cheaper every day, and let's hope that this trend does not change.
Many new computer models already contain this type of drive, manufacturers themselves have optimized the operating system to work efficiently with a solid state drive.
Of course, you need to choose the optimization method yourself, and we only gave the most important tips on how to do this without losing important data when transferring the system to an SSD.
compsch.com
How to set up an SSD drive under WIndows 7
For many users, replacing a hard drive with an SSD is the most cost effective PC upgrade. In terms of reading information, the SSD drive is many times faster, therefore, the performance of the computer is significantly increased. But they have one drawback - the limitation on the number of rewrite cycles that is typical for flash drives.

Configuring an SSD under windows 7 is necessary as you need to minimize unnecessary write cycles to flash memory cells in order to increase the life of your SSD.
If you have windows 10 installed, then it already automatically detects SSD drives and makes its own adjustments to their work to achieve maximum performance. Therefore, on windows 10, setting up ssd is not so important and is performed at the operating system level.
Disable Disk Defragmenter
During the defragmentation process, logically interconnected data blocks that are scattered throughout the media are arranged in a single sequence. SSD drives do not need to be defragmented. If for HDD hard drives defragmentation can increase efficiency in read speed and thereby speed up PC performance, then in the case of SSD this process can only do harm.
Disabling Perfetch and SuperFetch
The Perfetch folder is designed to speed up windows loading and launching programs. The folder contains information about frequently used programs on the computer and stores them in the initial (system) part of the hard drive.
The SuperFetch service monitors the programs that you frequently use and loads them into random access memory (RAM) when the computer starts up, so that when you access them, they start up faster. Thus, when you run a program, the computer begins to read its files faster from RAM than from the hard drive.
But given the high read speeds of SSDs, these features are redundant.
To disable them, go to the windows registry editor with administrator rights.
In the "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE" directory, find the "SYSTEM/CurrentControlSet/Control/SessionManager/MemoryManagement/PrefetchParameters" key and change the "Enable Prefetcher" and "Enable Superfetch" values to "0".
Disabling ReadyBoot
ReadyBoost speeds up windows and works together with the SuperFetch service. If SuperFetch loads files of used programs into random access memory (RAM), then ReadyBoost uses the flash drive as a cache memory for a slow hard drive.
To disable ReadyBoost, follow these steps:
- Start;
- Control Panel;
- System and safety;
- Administrative tools;
- Performance Monitor;
- on the left side, expand the "Data Collector Groups" section and select "Launch Event Tracking Sessions";
- double click on "ReadyBoost";
- Tracking sessions;
- uncheck the box next to "Enabled".
Disabling or moving the paging file to the HDD
The paging file increases the computer's cache size. In the event that there is not enough physical RAM memory, the windows operating system moves some of the data out of RAM and thus prevents software or system errors.
If the computer is equipped with a small SSD and a traditional HDD, then the swap file can be placed on the SSD. If you have windows x64 installed, you can disable the paging file.
TRIM function
In the windows 7 operating system, it is important to check if the TRIM function is enabled. Note that this function informs the SSD drive which area on the disk is no longer in use and can be cleaned up. If the feature is disabled, it may result in slower performance of the SSD.
To check:
- go to command prompt as administrator;
- enter the command "fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify";
- if DisableDeleteNotify = 0 appears after execution, then the service is enabled.
Disabling Sleep (Hibernation)
The hibernation feature clearly reduces the time it takes windows to start up from the hard drive. Compared to hard drives, SSD drives are much faster in terms of reading information, which makes the startup process much shorter. Therefore, hibernation mode in computers with SSD does not bring tangible benefits and can be disabled.
When you enter sleep mode, all data from RAM is saved to your hard drive in the hiberhil.sys file, which is quite a decent size. Especially true for smaller SSDs, disabling hibernation frees up valuable space on the SSD.
To turn it off, use the Win + R keys to launch the command prompt as an administrator and type the command "powercfg -h off".
AHCI mode
For the full operation of the SSD drive, including enabling the TRIM function, you need to enable AHCI mode in the BIOS. If you just change the mode, then after turning on the windows boot process may be interrupted by an error (blue screen).
For correction:
- go to the windows registry editor as an administrator;
- look for the entry "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/System/CurrentControlSet/Services/Msahci" or "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/System/CurrentControlSet/Services/lastorV";
- double click on "Start" and change the value to "0";
- restart your computer;
- Change the BIOS mode of the SATA controller to AHCI.
InstComputer.ru
Setting up windows 7 for optimal work with an SSD drive
Here I will not tell you what an SSD is and how it is better / worse than a regular hard drive. I recommend that you first read the previous articles on this topic, which talk about the Combination of SSD and HDD drive for a desktop computer and recommendations for installing MS windows 7 on an SSD. If you have followed the advice in these articles, windows 7 should already be flying on your SSD-equipped PC. You will not be able to speed it up even more, even after optimizing many system functions, the results of which have a much greater positive effect on the HDD than the new SSDs. These features are discussed in 4 parts of the article "Setting up windows 7 from A to Z". In the same article, I want to describe those manipulations that are designed to extend the life of your solid state drive (by reducing the load on it) and free up about 5-10 extra gigabytes of space, which is very important in our case. Today we make all changes manually. If the process is not important to you, download the SSD Tweaker (Pro) program, which will perform steps 3,5,6 for you. and much more... What are we going to do today? Here is a summary:
- 1. Move the paging file to another disk (HDD)
- 2. Disable the creation of system restore points
- 3. Turn off the indexing function
- 4. Turn off the defragmentation service
- 5. Turn off the Hibernation feature
- 6. Disable Prefetch and Superfetch
First. Transferring the swap file will increase the amount of free space on the SSD exactly as much as this file itself weighs. Let it lie better on the HDD, where there is much more space (especially since the paging file is used only when there is a lack of RAM and only 5% of applications are required). We go along the "Start" path - right click on "Computer" - "Properties" - on the left select "Advanced system settings" and look at the following three screenshots (stolen from my other article): As a result, our paging file will become a fixed size, which will prevent its constant fragmentation; and will be stored on another drive (not SSD).
Second. Disable system creation of restore points. I don’t know how anyone, but it’s always been easier for me to roll back a fresh operating system from an image than to guess at which restore point it was 100% working. But in the case of SSD, everything is much more categorical. The restore point creation feature MUST be disabled. About a year ago, it became known that when the creation of restore points is enabled, the work of the "TRIM" function, which is vital for the SSD, is blocked. Due to this, over time, there is a gradual degradation of the speed of the drive. Well, two auxiliary factors - as a result, we will reduce the load and increase the amount of free space on the SSD. We pass along the previous path: "Start" - right click on "Computer" - "Properties" - on the left select "System Protection" and look at the following screenshot:
Third. The indexing feature was created to speed up searches in windows. Its job is that during inactivity, the operating system checks, updates and saves indexes for all files on your disks in order to quickly display the results of possible search queries. Thus, the load on the disk increases (or rather, the load time increases) and the index files themselves take up a certain amount of space on it. I don’t use windows search at all, and thanks to the high response speed of the SSD, this function simply does not make sense. Open File Explorer, right-click on the SSD - Properties - uncheck "Allow the contents of files on this drive to be indexed"

Fourth. The defragmentation service is unnecessary on an SSD (due to a completely different mechanism of operation than on an HDD) and is contraindicated (NAND memory, which is used in an SSD, has a limited number of rewrite cycles). If it so happened that windows 7 left this feature enabled (usually when installing the operating system on a solid state drive, the defragmentation service is disabled by default) - go along the path: "Start" - "Run" - enter "services.msc" (without quotes) , look for the "Disk Defragmentation" service in the list, double-click on it, select "Disabled" in the "Startup Type" field, click "Stop" - "Apply" - "OK" in order.
Fifth. hibernation. This function is only needed when using an HDD and is mainly used on laptops. This is a kind of "Deep Sleep Mode", in which all the contents of the RAM are written to disk to speed up the further loading of the system. This is not relevant for SSDs, and besides, disabling Hibernation will free up about 2 GB of disk space ... Click "Start" - "Run", enter the text "cmd" (without quotes), in the window that appears, write the command "powercfg -h off " (without quotes), press the "Enter" button.
Sixth. Prefetch - Preload frequently used applications and libraries into RAM. When using an SSD, the performance gain is not felt. Disabling frees up RAM space and reduces the number of requests to the drive. Superfetch - caching frequently used files. It's completely useless on an SSD. To disable both functions, go to "Start" - "Run" - enter "regedit" (without quotes), in the windows registry editor we go along the path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\MemoryManagement\PrefetchParameters right click on each of the items : "EnablePrefetcher", "EnableSuperfetch", select "Change", enter the number "0":

rapidsoft.org
Setting up an SSD for windows 7 - optimization, program, TRIM
Windows 7 was not originally designed to run on an SSD. Since they appeared, Microsoft has released numerous updates designed to improve the operation of the OS on solid state drives. However, you need to carry out additional optimization manually, which gives a much greater effect.
SSD
A Solid State Drive is a storage device based on flash memory and a control controller.
They are widely used in computing and have some advantages over HDD:
- high speed;
- impact resistance;
- heat resistance;
- small size and weight;
- noiselessness.

In windows 8 and above, they work stably and quickly, but under older operating systems, problems with wear and speed are inevitable. To avoid this, you need to optimize the parameters, which is what this article is about.
What gives optimization
Windows 7 has several services that increase the performance of conventional hard drives. But with SSD, they not only do not bring benefits, but interfere with work and significantly reduce the life of the device. Setting up Windows 7 on an SSD nullifies all attempts by the OS to destroy it, and allows you to achieve greater performance.
Even if we compare the maximum read / write speed declared by the manufacturer, the difference will be huge.
The linear speed of solid state drives is 3-4 times higher.
It's rare for a typical hard drive to achieve 180 MB/s read speeds. At the same time, he does not spend time moving the head, but focuses on reading data.

For a regular SSD, such as the Kingston SKC380S3, the limit is 550 MB/s. for reading and 520 for writing. In linear read mode, it uses all channels and reads data in large blocks. However, if we take a closer look at performance, the superiority of SSDs will be even more impressive.
When testing the speed of reading blocks of 512 KB in size (small files), the gap becomes even larger. The SSD does not spend much time looking for a block, as a result of which its speed is still within 500 MB / s. The hard drive spends more time moving the head than reading files. Its speed is reduced three times and averages 60 MB / s, which is 8 times slower than SSD.

Photo: 512 KB random block reading test
If we go deeper into the tests and check the speed on blocks of 4 KB, then the SSD will bypass the hard drive 50 times. Loading the OS, copying documents, small images and launching programs all correspond to this mode of operation. In addition, SSDs can handle multiple requests at the same time, while HDDs are single-threaded.
Video: how to properly set up the system for work
Setting up an SSD in windows 7
This process requires patience and includes the following procedures:

Setting up windows 7 for SSD begins with the firmware of the drive. All manufacturers regularly release new versions of software for their devices, in which errors and weaknesses of previous versions are eliminated. You can download it from the official websites of the brand. The software package also usually comes with instructions for installing it and updating the firmware.
AHCI and TRIM
The SATA interface has many features that speed up data transfer. In order for them to become available, you need to enable the AHCI controller, since most PCs are still configured to work with the outdated ATA controller by default. You can switch to AHCI either automatically or manually.
Automatic switching:

The next time you start windows 7 will do the rest of the work itself. If for some reason the utility does not work, then you can do everything manually.
Manual switching:

As a result, after a reboot, the AHCI controller will be visible in the device manager.

AHCI is over, the TRIM command is next. It helps the OS notify the SSD about what data the file system no longer contains and what the drive can delete. That is, this command removes garbage and does not allow it to reduce the performance level.
You can enable TRIM if the following conditions are met:
- the SSD controller supports this command;
- SATA mode: AHCI enabled.
If the conditions are met, you can proceed to enable TRIM:

Disabling system protection
The instruction is quite simple:

It is important to understand that by disabling protection, the OS will not make restore checkpoints and, in the event of a failure, it will be impossible to resort to restoring windows. Therefore, it is worth using software from other developers to provide the recovery function, for example, Acronis True Image.
Disable disk indexing
Indexing is carried out only in order to speed up the search process on the hard disk. Given the multi-threading of the SSD and its speed, the indexing and searching service is not needed.
Disable search like this:

Disable indexing like this:
- open "Computer";
- right-click on the section -> Properties;
- at the very bottom of the window that opens, uncheck the box "allow indexing ...";
- apply and close the window.
Along the way, you can also disable defragmentation, which is useless on SSD drives due to quick access to cells.
You can do this:

Disabling paging
The paging file is necessary for running programs that need a large amount of memory. If there is not enough RAM, then temporary data is loaded into this file. You can disable it only if the computer has enough RAM installed (at least 8 GB). Otherwise, it is better to move the swap to another partition, i.e. to the hard drive.
Shutdown:

Disabling hibernation
Hibernation or deep sleep of the computer was invented by Microsoft so that the computer does not spend a lot of time starting up. This feature allows you to power off your computer without closing applications. When you wake up again, all programs continue to work.
At the same time, when the PC goes to sleep, a large amount of data is written to the drive and the SSD wears out faster. Also, for many, hibernation is not necessary, since a PC with a solid state drive boots very quickly.
If you decide to disable hibernation, then you can do it like this:

SSD Tweak Utility
To optimize your system to use the SSD drive automatically, you can use the SSD Tweak Utility. The program allows you to quickly and easily do everything that was described above, except for enabling AHCI mode. The program is published with a different set of tools.

There is a free version with a basic set of functions:
- disabling defragmentation;
- disable recovery;
- stop indexing.
Other features available in the paid version of Tweaker Pro include:
- enabling and disabling services;
- setting hibernation options;
- verification and experimental optimization of the TRIM command.
The program also allows deeper customization, which includes many more parameters. After starting the program in the right part of the window, you can see a detailed description and tips on setting up the system.

To start optimization, just press the big button in the middle of the program window - auto-tuning configuration. The utility itself will configure the main parameters and provide a report.
Setting up and optimizing windows 7 for SSD is not a quick process, accompanied by several system reboots and visits to the BIOS. However, if you do not configure it, do not disable unnecessary services, then after a few months the once-fast SSD may exhaust its supply of write cycles and stop working.
Need USB WIFI adapter for LG TV? Find out how to choose here.
What to do if the laptop does not see wifi? All answers are here.
proremontpk.ru
How to optimally configure an SSD drive for windows 7

In this article, we will talk about setting up an SSD drive for the windows 7 operating system. What needs to be done for this and why in general to configure an SSD device in windows 7, we will consider further.
So, quite recently, my friend bought a powerful computer. And for greater speed, it was decided to install an SSD drive there to install the operating system on it.
Let's see how an SSD differs from a conventional HDD. As Wikipedia tells us:
SSD - Solid state drive (English solid-statedrive, SSD) - computer non-mechanical storage device based on memory chips. In addition to them, the SSD contains a control controller.
Unlike SSD, HDD is a hard disk drive or HDD (English hard (magnetic) diskdrive, HDD, HMDD), a hard drive, in computer slang "hard drive" - a random access storage device (information storage device), based on principle of magnetic recording. It is the main storage medium in most computers.
The main advantage of an SSD over a standard hard drive is the absence of mechanical (moving) parts, which increases its reliability. Also, the advantage of an SSD is its high speed of operation, it heats up less and does not make any sounds during operation. But SSD, in addition to many advantages, there are also disadvantages. The main disadvantage of SSD is the limited number of write/rewrite cycles. Conventional (MLC, Multi-level cell, multi-level memory cells) flash memory allows you to write data about 10,000 times. More expensive types of memory (SLC, Single-level cell, single-level memory cells) - about 100,000 times. In order to reduce the number of accesses to the SSD drive and, accordingly, extend its life, it needs to be fine-tuned. Well, one more drawback is incompatibility with old OS (below windows Vista).
Next, we will consider what exactly needs to be done to configure a solid-state drive under the windows 7 operating system. Since I didn’t take screenshots when I set up an SSD for a friend, I will perform these settings on my old computer with a regular HDD.
So let's go.
Point one: turn off hibernation. You need to disable it for the reason that every time the computer switches to this mode, a large amount of information is written to the hard disk, and I always disable it, because sometimes it is difficult to exit this mode. In addition, by disabling hibernation, we will free up space on the system disk approximately equal to the amount of RAM. Hibernation is needed to quickly load the operating system, but since we have an SSD drive installed, windows loads in just 5-10 seconds anyway. To disable hibernation, run the command line (Start - Run here we write the cmd command). On the command line, write powercfg.exe / hibernate off . After restarting the computer, you will see the freed space on the system drive.

Or we go to "Start" - "Control Panel" - "Power Options" - "Setting up a power plan" - "Change power settings" - we find the item "Sleep", open it, the item "Hibernation after" enter the value "0".
Point two: we transfer the folder for storing temporary TEMP files to a regular HDD.
To do this, right-click on the "My Computer" icon - "Properties" - "Advanced system settings" - the "Advanced" tab - the "Environment Variables" button - and change the path of the TMP and TEMP variable to another folder (I created it in advance on the disk D:\).

Point three: disable "System Protection".
To disable system protection, right-click on "My Computer" - "Properties" - "System Protection" - the "System Protection" tab - "Configure" - "Disable System Protection".

If the system protection is disabled, in case of its failure, we will not be able to recover from the backup, but we do not need it, because the system is installed in some 10-15 minutes.
Point four: transfer the swap file to the second hard drive. To do this, right-click on "My Computer" - "Properties" - "Advanced system settings" - the "Advanced" tab - the "Performance" section - the "Settings" button. Here we change the parameters as in the figure (depending on the free space on the D:\ drive, you can set a larger volume).

Item five: disabling indexing.
Indexing is necessary to speed up disk searches. But, for example, I have never used the search, besides, search on an SSD works quickly even without it. Therefore, this option can be safely disabled. To do this, go to "My Computer", right-click on the C:\ drive, item of the drop-down menu "Properties". In the "General" tab, uncheck the box "Allow the contents of files on this drive to be indexed in addition to file properties."
Or you can remove indexing for all drives by disabling the "windowsSearch" service. To do this, go to "Control Panel" - "Administration" - "Services" - find our service and double-click on it - select the "Manual" startup type and click the "Stop" button.
Point six: disable Preftch and RedyBoot.
Prefetch is a technology that allows you to speed up the loading of windows by proactively reading data from the disk. For SSD, it is not needed, because SSD already has a high speed of random data reading.
To disable Prefetch, launch the registry editor (Start - Run - write regedit and press Enter). Next, open the registry branch:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINES\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
and change the value of the Enable Prefetcher key to "0".
RedyBoot is an add-on for Prefetch. In order to turn it off, we follow the path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINES\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\WMI\Autologger\ReadyBoot
Here we change the value of the Start parameter to "0".
Point seven: transferring application caches. Here, first of all, it means transferring the browser cache to a second hard drive. I will not describe how to do this, because each browser has its own way. Therefore, if you decide to transfer the cache to the second hard drive, then Google will help you. But I would not do this at all, because we installed the SSD to speed up the work, and transferring the cache to the second HDD will not add speed to us. In general, it's up to you.
It is also necessary to turn off defragmentation, but for windows 7, unlike Vista, defragmentation is turned off automatically when installed on an SSD (the same is written about Prefetch and RedyBoot, but they were not set to “0” for me, so check) .
That's all. On the Internet you can find more tips on optimizing SSD for windows 7, but they are no longer as important as these. However, even without such a setting, the SSD will last quite a long time, but if you want to extend its life as much as possible, then I recommend that you follow the above points. Plus, we will free up some space on the system disk, and given the cost of a gigabyte of memory for an SSD, this is quite justified.
Windows 7 was not originally designed to run on an SSD. Since they appeared, Microsoft has released numerous updates designed to improve the operation of the OS on solid state drives. However, you need to carry out additional optimization manually, which gives a much greater effect.
SSD
A Solid State Drive is a storage device based on flash memory and a control controller.
They are widely used in computing and have some advantages over HDD:
- high speed;
- impact resistance;
- heat resistance;
- small size and weight;
- noiselessness.
- the SSD controller supports this command;
- SATA mode: AHCI enabled.
In Windows 8 and above, they work stably and quickly, but under older OS, problems with wear and performance are inevitable. To avoid this, you need to optimize the parameters, which is what this article is about.
What gives optimization
Windows 7 has several services that increase the performance of conventional hard drives. But with SSD, they not only do not bring benefits, but interfere with work and significantly reduce the life of the device. Setting up Windows 7 on an SSD nullifies all attempts by the OS to destroy it, and allows you to achieve greater performance.
Are SSDs faster?
Even if we compare the maximum read / write speed declared by the manufacturer, the difference will be huge.
The linear speed of solid state drives is 3-4 times higher.
It's rare for a typical hard drive to achieve 180 MB/s read speeds. At the same time, he does not spend time moving the head, but focuses on reading data.

For a regular SSD, such as the Kingston SKC380S3, the limit is 550 MB/s. for reading and 520 for writing. In linear read mode, it uses all channels and reads data in large blocks. However, if we take a closer look at performance, the superiority of SSDs will be even more impressive.
When testing the speed of reading blocks of 512 KB in size (small files), the gap becomes even larger. The SSD does not spend much time looking for a block, as a result of which its speed is still within 500 MB / s. The hard drive spends more time moving the head than reading files. Its speed is reduced three times and averages 60 MB / s, which is 8 times slower than SSD.

If we go deeper into the tests and check the speed on blocks of 4 KB, then the SSD will bypass the hard drive 50 times. Loading the OS, copying documents, small images and launching programs all correspond to this mode of operation. In addition, SSDs can handle multiple requests at the same time, while HDDs are single-threaded.
Video: how to properly set up the system for work
Setting up an SSD in Windows 7
This process requires patience and includes the following procedures:

Setting up Windows 7 for an SSD starts with flashing the drive. All manufacturers regularly release new versions of software for their devices, in which errors and weaknesses of previous versions are eliminated. You can download it from the official websites of the brand. The software package also usually comes with instructions for installing it and updating the firmware.
AHCI and TRIM
The SATA interface has many features that speed up data transfer. In order for them to become available, you need to enable the AHCI controller, since most PCs are still configured to work with the outdated ATA controller by default. You can switch to AHCI either automatically or manually.
Automatic switching:

The next time you start Windows 7 will do the rest of the work itself. If for some reason the utility does not work, then you can do everything manually.
Manual switching:

As a result, after a reboot, the AHCI controller will be visible in the device manager.

AHCI is over, the TRIM command is next. It helps the OS notify the SSD about what data the file system no longer contains and what the drive can delete. That is, this command removes garbage and does not allow it to reduce the performance level.
You can enable TRIM if the following conditions are met:
If the conditions are met, you can proceed to enable TRIM:

Disabling system protection
The instruction is quite simple:

It is important to understand that by disabling protection, the OS will not make restore checkpoints and, in the event of a failure, it will be impossible to resort to Windows recovery. Therefore, it is worth using software from other developers to provide the recovery function, for example, Acronis True Image.
Disable disk indexing
Indexing is carried out only in order to speed up the search process on the hard disk. Given the multi-threading of the SSD and its speed, the indexing and searching service is not needed.
Disable search like this:

Disable indexing like this:
- open "Computer";
- right-click on the section -> Properties;
- at the very bottom of the window that opens, uncheck the box "allow indexing ...";
- apply and close the window.
- by going to the tab Service -> Optimize;
- by selecting a section and clicking change settings;
- by unchecking the "Run as scheduled" checkbox.

Along the way, you can also disable defragmentation, which is useless on SSD drives due to quick access to cells.
You can do this:
Disabling paging
The paging file is necessary for running programs that need a large amount of memory. If there is not enough RAM, then temporary data is loaded into this file. You can disable it only if the computer has enough RAM installed (at least 8 GB). Otherwise, it is better to move the swap to another partition, i.e. to the hard drive.
Shutdown:

Disabling hibernation
Hibernation or deep sleep of the computer was invented by Microsoft so that the computer does not spend a lot of time starting up. This feature allows you to power off your computer without closing applications. When you wake up again, all programs continue to work.
At the same time, when the PC goes to sleep, a large amount of data is written to the drive and the SSD wears out faster. Also, for many, hibernation is not necessary, since a PC with a solid state drive boots very quickly.
If you decide to disable hibernation, then you can do it like this:

SSD Tweak Utility
To optimize your system to use the SSD drive automatically, you can use the SSD Tweak Utility. The program allows you to quickly and easily do everything that was described above, except for enabling AHCI mode. The program is published with a different set of tools.

There is a free version with a basic set of functions:
- disabling defragmentation;
- disable recovery;
- stop indexing.
Other features available in the paid version of Tweaker Pro include:
- enabling and disabling services;
- setting hibernation options;
- verification and experimental optimization of the TRIM command.
The program also allows deeper customization, which includes many more parameters. After starting the program in the right part of the window, you can see a detailed description and tips on setting up the system.

To start optimization, just press the big button in the middle of the program window - auto-tuning configuration. The utility itself will configure the main parameters and provide a report.
Setting up and optimizing Windows 7 for SSD is not a quick process, accompanied by several system reboots and visits to the BIOS. However, if you do not configure it, do not disable unnecessary services, then after a few months the once-fast SSD may exhaust its supply of write cycles and stop working.
To prevent this from happening, after each reinstallation of the system, it is necessary to optimize it. This can be done either manually or automatically using the SSD Tweaker utility.